Risk management
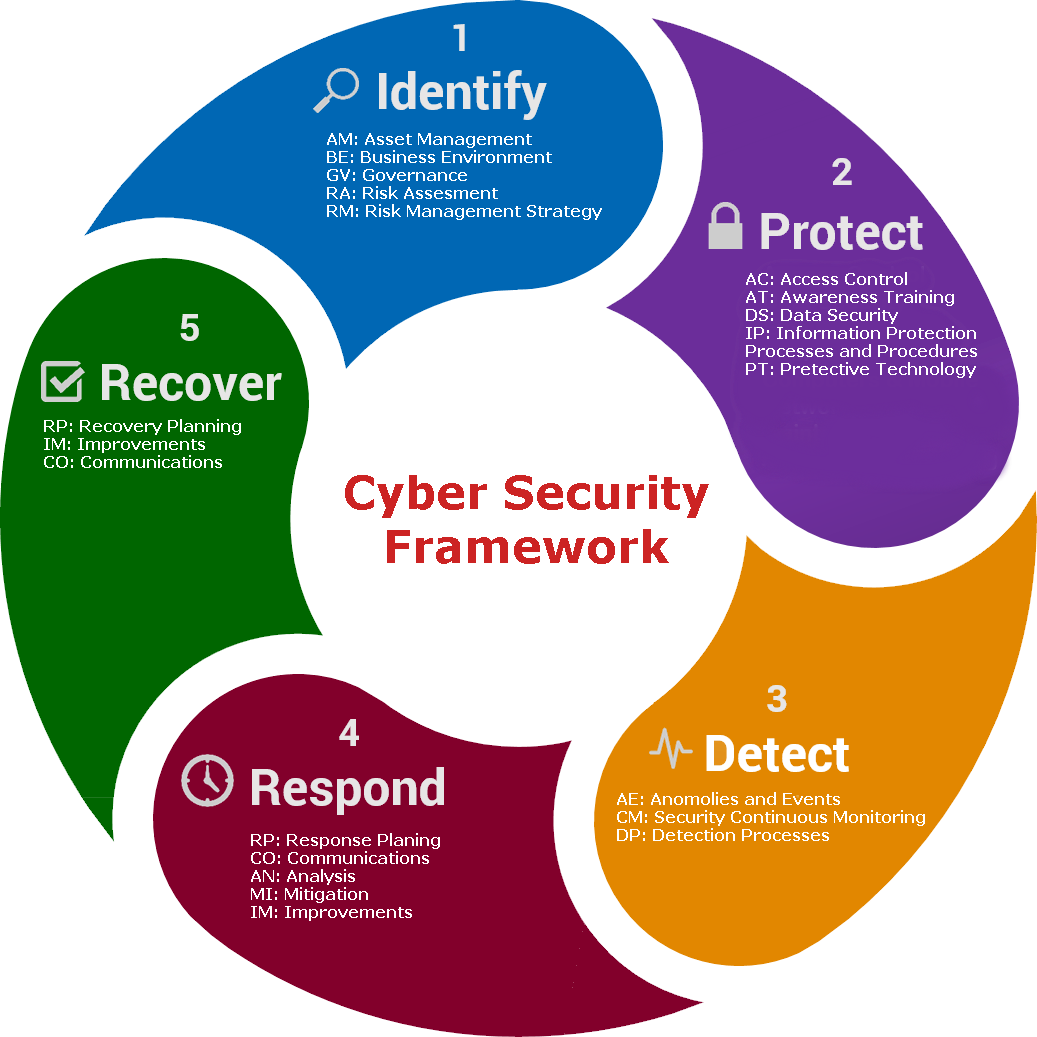
- Risk management is part of information security .
- That means preventing or reducing the unauthorized access to data, or data deletion, or data modification or any inconvenient thing do for the information
- So this Information security’s primary focus on confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data
- We also known as the CIA triad
CIA Triad
- Confidentiality
- That means Computer-related assets are only available to authorized parties.
- Only those parties should have access to something.
- So Controlling the access based on the need is Confidentiality.
- We use Authorization, authentication, encryption concepts to do this.
- Integrity
- It Assure that the data or information systems can be trusted (hashing,signing)
- So the data should be Unmodified, Meaningful and usable
- Availability
- This means Data and information systems are available when required (monitoring, alerting,HA)
- So it needs to timely response to our requests
- So it should Control concurrency, support for simultaneous access with proper deadlock, and access management.
What is SSL Means?
- SSL which means Secure Sockets Layer
- That means a protocol which we can use to establish authenticated and encrypted link between network.
- This is a cryptographic protocol which used to provide security over internet communications
- So this SSL provides a secure channel between two machines or devices operating over the internet or an internal network.
- As this SSL is a security protocol, it describe how algorithms should be used.
Example
- One common example is SSL use to secure communication between a web browser and a web server.
- That means HTTPS
- Hyper text transfer protocol secure
- As like HTTP, HTTPS is application layer protocol
- So it is transferring web pages
- Using HTTP is not secure method.
- So we can use HTTPS which is secure protocol. So data will be encrypted and send.
- So if attacker trying to get information, they can also get encrypted data.
- Main thing is this HTTPS websites includes SSL/TLS certificate which is signed by a CA.
- we can use this method for online payments like credit card transactions
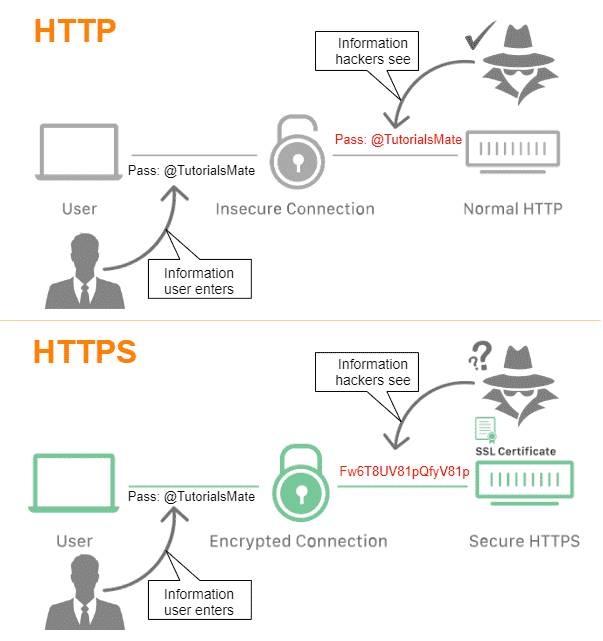
How Do I Know a Website is Secure with SSL?
URL with the other one is not secure
Label HTTPS Sites as ‘Secure.’
Why we use SSL?
- Transferring sensitive information over a network can be risky
- Because You can’t always be sure the entity you are communicating is real one.
- Also there is possibility that an unauthorized third party is reading our data.
- If attacker access our data, he can modify the data, before sending it to the receiver.
- We can use this secure method to transfer sensitive data Like payments information.
- In online transactions need to be more secure. So we need to use this kind of secure method to transfer information.
- Protect the data of you and your users
- This will encrypt the data and transfer.
- That means any malicious trying to get this data, he will also get the encrypted data.
- Which is not usable.
- Our users can feel safe that their data is in safe
- Showing your users you can be trusted
- This method is providing a SSL certificate
- So users know they can trust you.
How does the SSL provide data security?
- Authenticating
- It ensure the identity of the other party which is authenticating the user.
- Two parties need to authenticate weather they have access to communicate
- Establish an encrypted connection
- Once these users are authenticated, SSL provides an encrypted connection between them for secure message transmission.
- Send encrypted data
- Here encryption algorithms are using with SSL
- So This ensure that data doesn’t modified during transit.
What is SSL Handshake?
- The SSL/TLS handshake enables client and server validate each other and start communicating through the secure SSL/TLS tunnel.
- That means this handshake is done when client and server trying to communicate with each other for the first time
- So before starting this SSL/TLS handshake that TCP connection need to be already established
Uses of SSL
- Online credit card transactions or other online payments.
- Office Communications Servers – Webmail servers like Outlook
- Cloud-based computing platforms – virtualization applications
- Hosting control panel login – like cPanel
1-Way and 2-Way SSL
1-way SSL
- This is the common way to verify the authenticity of the website that you are trying to access.
- In this authentication, the client is never verified.
- It only validate the server, to ensure that the data is sending from the valid server.
2-way SSL
- Here both the client and server exchange their certificates and verifies authenticity.
- After that Mutual trust is obtaining because CA is verifying both parties’ certificates.
What is a Certificate?
- Certificate is a digitally signed document that binds the identity of entity and its public key.
- SSL certificate we also known as a TLS or SSL/TLS certificate.
- Here TLS means -Transport Layer Security.
- This is also a protocol we use for authentication and encryption.
- Normally we say Certificates are data files that have encrypted cryptographic keys with additional information such as domain name, host name, and server details of organization
- Certificates can either be self-signed or issued by a Certification Authority (CA)
- Certification Authorities are entities that are trusted to issue valid certificates for other entities
Certificate contents

- Issuer
- The issuer is the CA that issued the certificate.
- If a user trusts the CA that issues a certificate, and if the certificate is valid, the user can trust the certificate.
- Period of validity
- A certificate has an expiration date, and this date is one piece of information that should be checked when verifying the validity of a certificate.
- Subject
- The subject field includes information about the entity that the certificate represents.
- Subject’s public key
- The primary piece of information that the certificate provides is the subject’s public key.
- All the other fields are provided to ensure the validity of this key.
- Signature
- The certificate is digitally signed by the CA that issued the certificate.
- The signature is created using the CA’s private key and ensures the validity of the certificate.
- Because only the certificate is signed, not the data sent in the SSL transaction, SSL does not provide for non-repudiation.
How to get a certificate?
- For the SSL certificate to be valid one, it need to obtain from a CA.
- CA is an outside organization and it is a trusted third party
- Client Generate the CSR which means certificate signing request
- Then Send CSR to the CA that means certificate authority
- The CA will also digitally sign the certificate with their own private key, allowing client devices to verify it.
- Once the certificate is issued, it needs to be installed and activated on the website’s server.
- So normally Web hosting services handle this for website operators.
- Once it’s activated on the origin server, the website will be able to load over HTTPS
- So then all traffic to and from the website will be encrypted and secure.
SSL CAs
- GoDaddy

- HubSpot

- Cloudflare

Self-signed SSL certificate

- Security certificate that is not signed by a certificate authority
- As the name says, this is a certificate that is generated for internal purposes and is not issued by a CA.
- website owner generates their own certificate,and this certificate that is not signed by a certificate authority
- These certificates are easy to make and do not need money
- We can create them using some tools
- OpenSSL,
- Java’s keytool
- Adobe Reader
- WolfSSL
- Apple’s Keychain
- But there is no outside authority to verify the origin server
- These self-signed SSL certificate are easy to customize
Difference Between Self-Signed and CA signed certificates


